PRESENTATION
Published on February 28, 2019
EXHIBIT 99.2
Heat Biologics Corporate PresentationFebruary 28, 2019

Forward Looking Statements This presentation includes statements that are, or may be deemed, ‘‘forward-looking statements’’ within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, as amended. In some cases, these forward-looking statements can be identified by the use of forward-looking terminology, including the terms “believes,” “estimates,” “anticipates,” “expects,” “plans,” “intends,” “may,” “could,” “might,” “will,” “should,” “approximately” or, in each case, their negative or other variations thereon or comparable terminology, although not all forward-looking statements contain these words. They appear in a number of places throughout this presentation and include statements regarding our intentions, beliefs, projections, outlook, analyses or current expectations concerning, among other things, our ongoing and planned discovery and development of drugs targeting cancer, the strength and breadth of our intellectual property, our ongoing and planned preclinical studies and clinical trials, the timing of and our ability to complete clinical trials and make regulatory filings and obtain and maintain regulatory approvals for our product candidates, our ability to partner our product development, the degree of clinical utility of our products, particularly in specific patient populations, expectations regarding clinical trial data, our results of operations, financial condition, liquidity, prospects, growth and strategies, the length of time that we will be able to continue to fund our operating expenses and capital expenditures, our expected financing needs and sources of financing, the industry in which we operate and the trends that may affect the industry or us. By their nature, forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties because they relate to events, competitive dynamics, and healthcare, regulatory and scientific developments and depend on the economic circumstances that may or may not occur in the future or may occur on longer or shorter timelines than anticipated. Although we believe that we have a reasonable basis for each forward-looking statement contained in this presentation, we caution you that forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance and that our actual results of operations, financial condition and liquidity, and the development of the industry in which we operate may differ materially from the forward-looking statements contained in this presentation as a result of, among other factors, the factors referenced in the “Risk Factors” section of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2017 and our quarterly report on Form 10-Q for the subsequent quarters (collectively, our “SEC Filings”). In addition, even if our results of operations, financial condition and liquidity, and the development of the industry in which we operate are consistent with the forward-looking statements contained in this presentation, they may not be predictive of results or developments in future periods. Any forward-looking statements that we make in this presentation speak only as of the date of such statement, and we undertake no obligation to update such statements to reflect events or circumstances after the date of this presentation, except as required by law.You should read carefully the factors described in the “Risk Factors” sections of our SEC Filings to better understand the risks and uncertainties inherent in our business. 2
Our Mission To improve patient outcomes by developing more effective immunotherapies designed to Turn “COLD” tumors “HOT 3
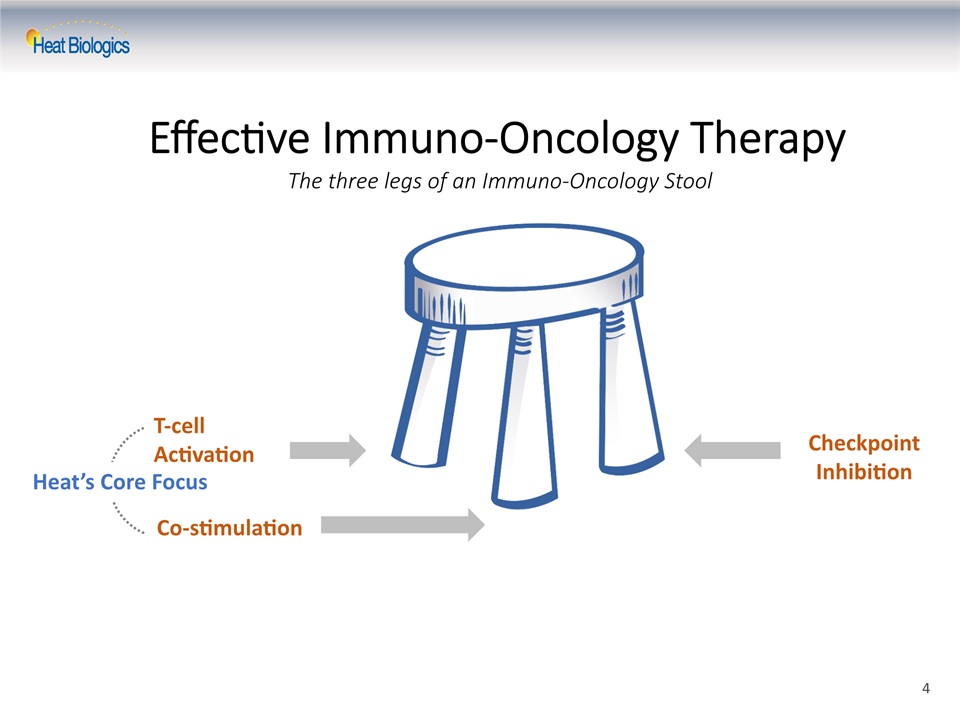
T-cell Activation Co-stimulation Heat’s Core Focus Checkpoint Inhibition Effective Immuno-Oncology TherapyThe three legs of an Immuno-Oncology Stool 4
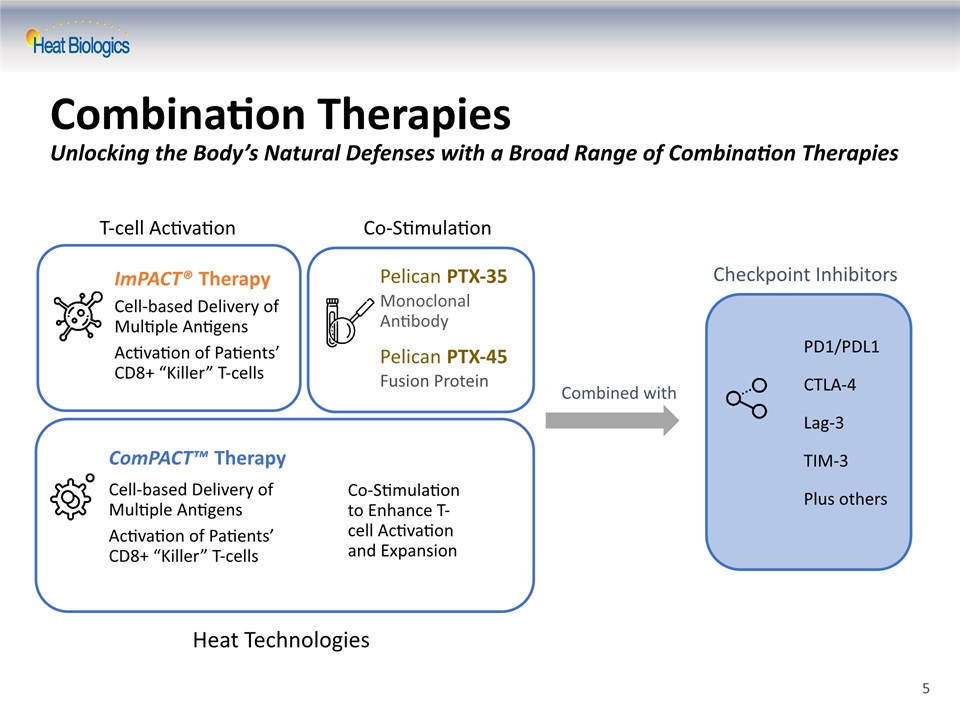
Combination TherapiesUnlocking the Body’s Natural Defenses with a Broad Range of Combination Therapies Checkpoint Inhibitors PD1/PDL1CTLA-4Lag-3TIM-3Plus others Combined with Co-Stimulation T-cell Activation Pelican PTX-35Monoclonal AntibodyPelican PTX-45Fusion Protein ImPACT® TherapyCell-based Delivery of Multiple Antigens Activation of Patients’CD8+ “Killer” T-cells ComPACT™ TherapyCell-based Delivery ofMultiple Antigens Activation of Patients’CD8+ “Killer” T-cells Co-Stimulation to Enhance T-cell Activation and Expansion Heat Technologies 5
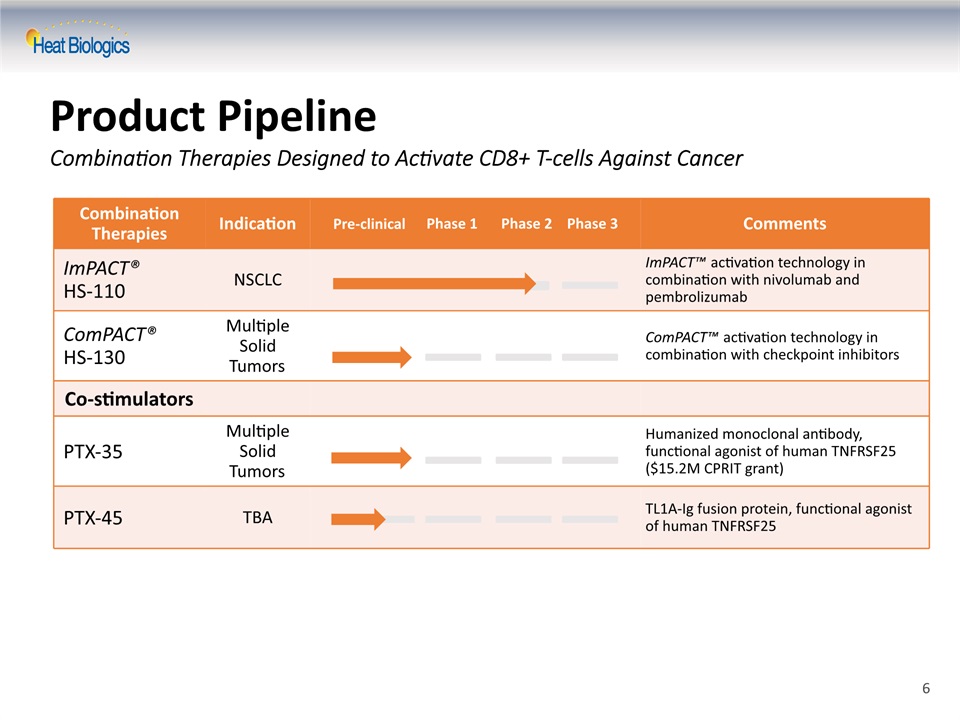
Product Pipeline Combination Therapies Designed to Activate CD8+ T-cells Against Cancer Combination Therapies Indication Comments ImPACT® HS-110 NSCLC ImPACT™ activation technology in combination with nivolumab and pembrolizumab ComPACT® HS-130 Multiple Solid Tumors ComPACT™ activation technology in combination with checkpoint inhibitors Co-stimulators PTX-35 Multiple Solid Tumors Humanized monoclonal antibody, functional agonist of human TNFRSF25 ($15.2M CPRIT grant) PTX-45 TBA TL1A-Ig fusion protein, functional agonist of human TNFRSF25 Pre-clinical Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 6
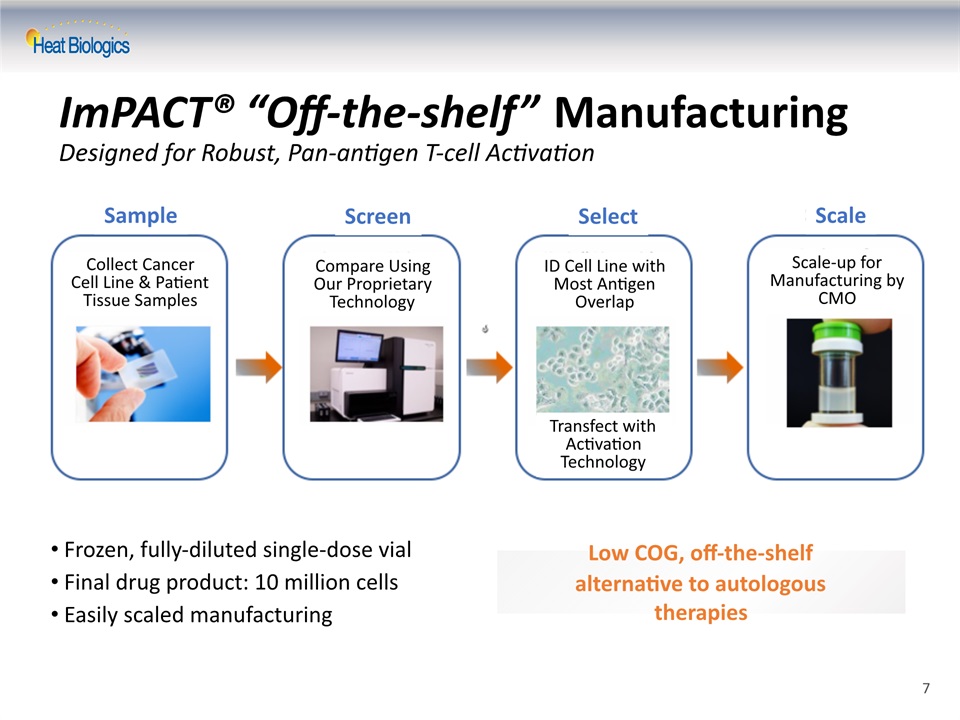
ImPACT® “Off-the-shelf” ManufacturingDesigned for Robust, Pan-antigen T-cell Activation Frozen, fully-diluted single-dose vialFinal drug product: 10 million cellsEasily scaled manufacturing Low COG, off-the-shelf alternative to autologous therapies 7 Sample Screen Select Scale Collect Cancer Cell Line & Patient Tissue Samples Compare Using Our Proprietary Technology ID Cell Line with Most Antigen Overlap Scale-up for Manufacturing by CMO Transfect with Activation Technology
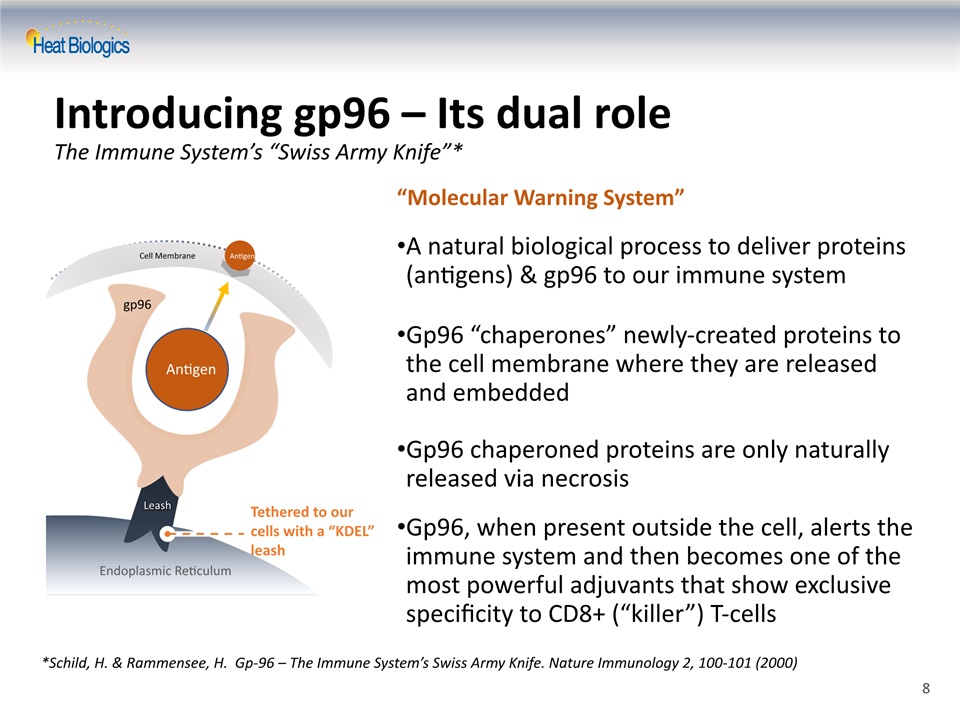
Introducing gp96 – Its dual roleThe Immune System’s “Swiss Army Knife”* *Schild, H. & Rammensee, H. Gp-96 – The Immune System’s Swiss Army Knife. Nature Immunology 2, 100-101 (2000) “Molecular Warning System” A natural biological process to deliver proteins (antigens) & gp96 to our immune systemGp96 “chaperones” newly-created proteins to the cell membrane where they are released and embeddedGp96 chaperoned proteins are only naturally released via necrosisGp96, when present outside the cell, alerts the immune system and then becomes one of the most powerful adjuvants that show exclusive specificity to CD8+ (“killer”) T-cells Tethered to our cells with a “KDEL” leash gp96 antigen Leash Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Membrane Antigen Antigen 8
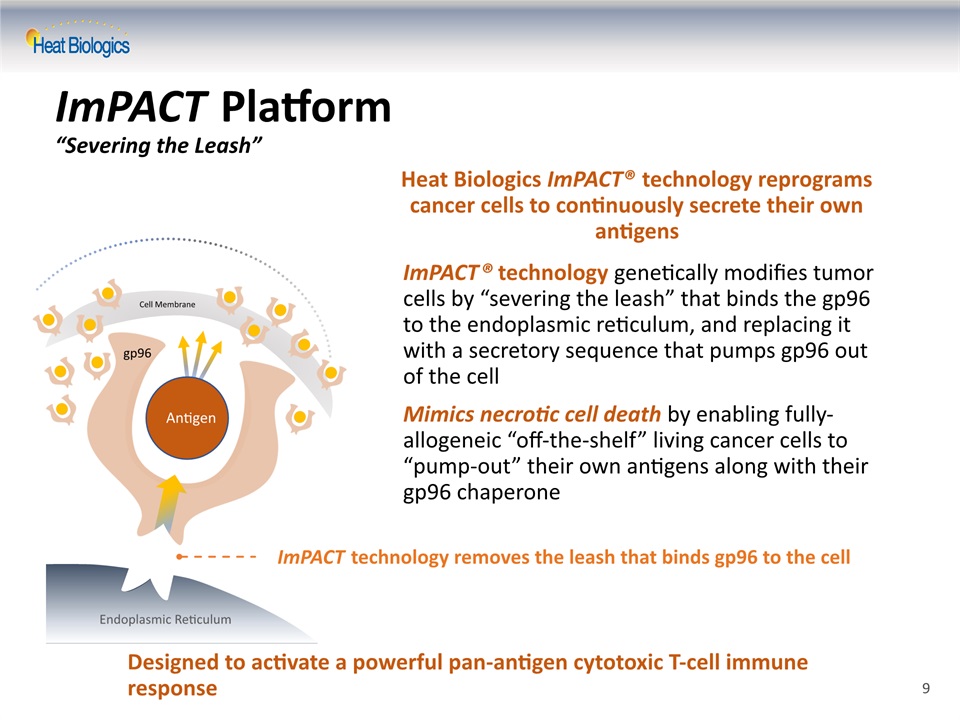
ImPACT® technology genetically modifies tumor cells by “severing the leash” that binds the gp96 to the endoplasmic reticulum, and replacing it with a secretory sequence that pumps gp96 out of the cellMimics necrotic cell death by enabling fully-allogeneic “off-the-shelf” living cancer cells to “pump-out” their own antigens along with their gp96 chaperone Heat Biologics ImPACT® technology reprograms cancer cells to continuously secrete their own antigens ImPACT technology removes the leash that binds gp96 to the cell ImPACT Platform“Severing the Leash” gp96 antigen Leash Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Membrane Antigen Designed to activate a powerful pan-antigen cytotoxic T-cell immune response 9
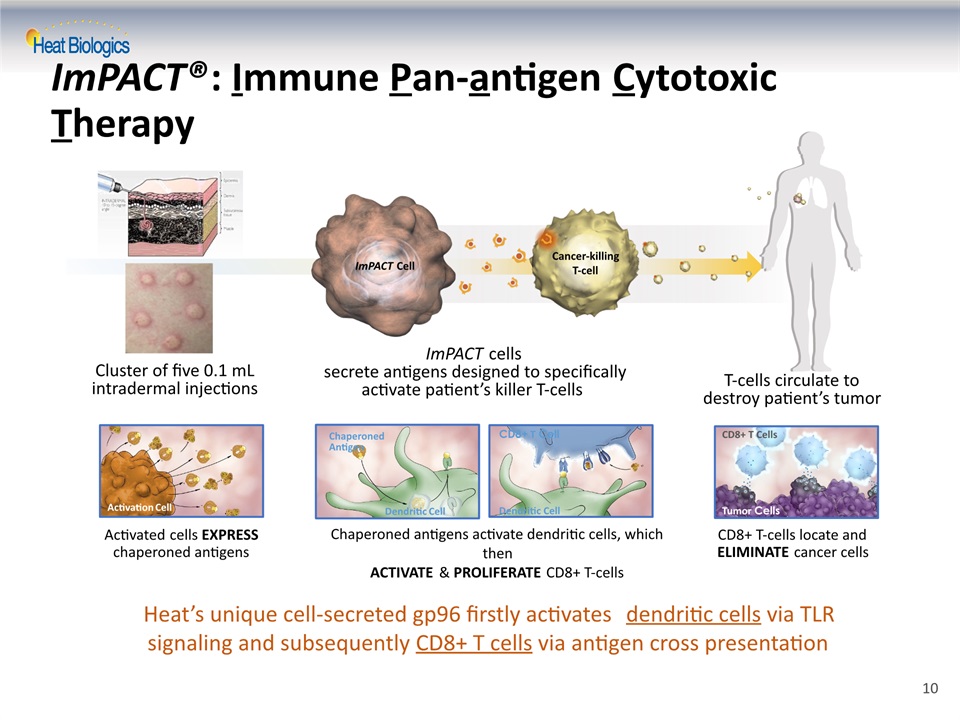
ImPACT®: Immune Pan-antigen Cytotoxic Therapy ImPACT Cell Cancer-killing T-cell ImPACT cells secrete antigens designed to specifically activate patient’s killer T-cells T-cells circulate to destroy patient’s tumor Cluster of five 0.1 mL intradermal injections Activated cells EXPRESS chaperoned antigens Activation Cell CD8+ T Cell Dendritic Cell Chaperoned antigens activate dendritic cells, which thenACTIVATE & PROLIFERATE CD8+ T-cells Dendritic Cell ChaperonedAntigen CD8+ T-cells locate and ELIMINATE cancer cells Tumor Cells CD8+ T Cells Heat’s unique cell-secreted gp96 firstly activates dendritic cells via TLR signaling and subsequently CD8+ T cells via antigen cross presentation 10
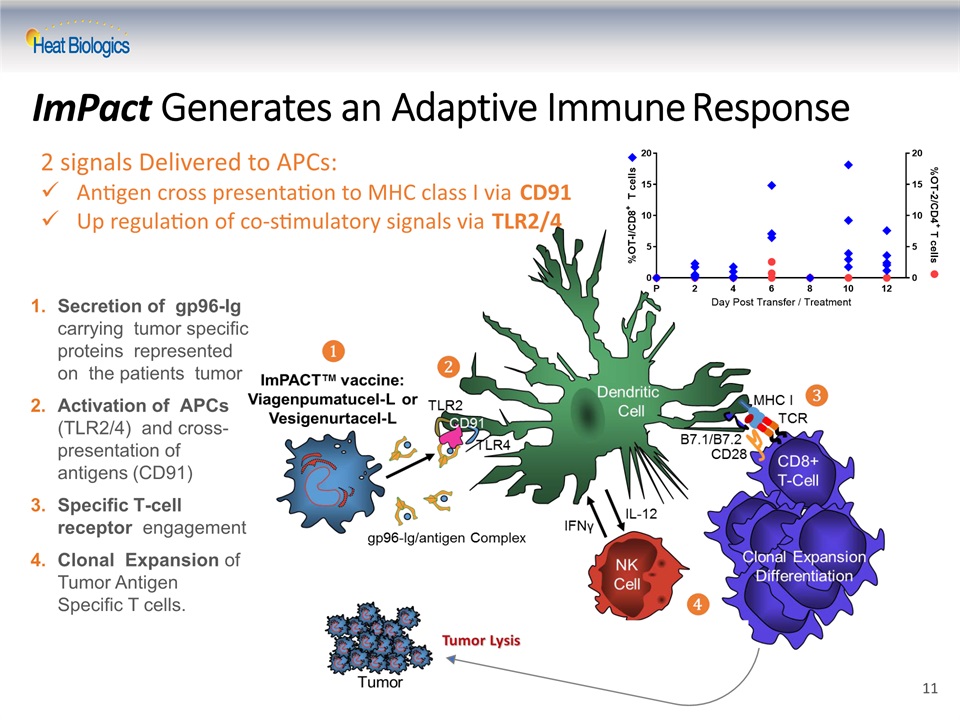
ImPact Generates an Adaptive Immune Response Secretion of gp96-Ig carrying tumor specific proteins represented on the patients tumorActivation of APCs (TLR2/4) and cross- presentation of antigens (CD91)Specific T-cell receptor engagementClonal Expansion of Tumor Antigen Specific T cells. 2 signals Delivered to APCs: Antigen cross presentation to MHC class I via CD91Up regulation of co-stimulatory signals via TLR2/4 11
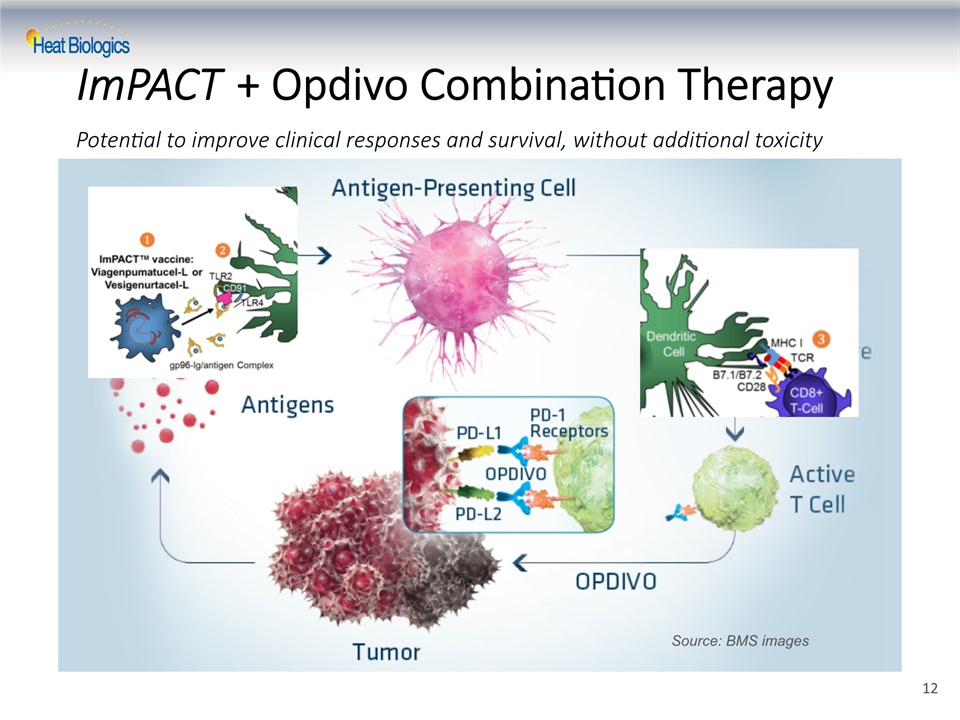
ImPACT + Opdivo Combination TherapyPotential to improve clinical responses and survival, without additional toxicity Source: BMS images 12
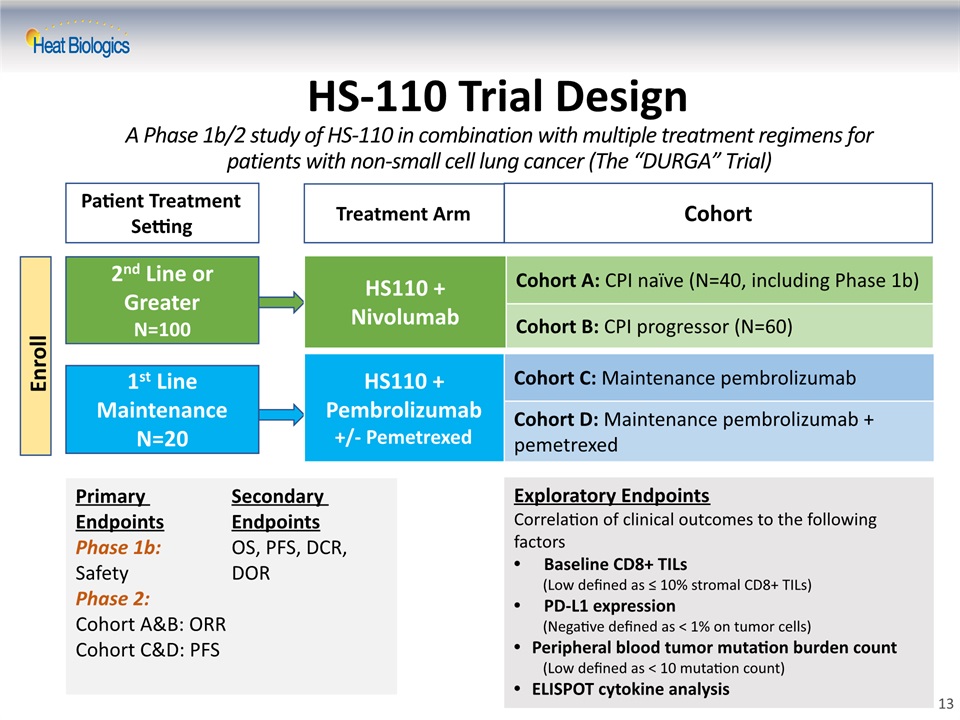
HS-110 Trial DesignA Phase 1b/2 study of HS-110 in combination with multiple treatment regimens for patients with non-small cell lung cancer (The “DURGA” Trial) Primary EndpointsPhase 1b: SafetyPhase 2: Cohort A&B: ORRCohort C&D: PFSSecondary EndpointsOS, PFS, DCR, DOR Exploratory EndpointsCorrelation of clinical outcomes to the following factorsBaseline CD8+ TILs (Low defined as ≤ 10% stromal CD8+ TILs)PD-L1 expression (Negative defined as < 1% on tumor cells)Peripheral blood tumor mutation burden count (Low defined as < 10 mutation count)ELISPOT cytokine analysis Patient Treatment Setting Treatment Arm Enroll 2nd Line or GreaterN=100 1st Line MaintenanceN=20 Cohort HS110 + Nivolumab Cohort A: CPI naïve (N=40, including Phase 1b) Cohort B: CPI progressor (N=60) HS110 + Pembrolizumab +/- Pemetrexed Cohort C: Maintenance pembrolizumab Cohort D: Maintenance pembrolizumab + pemetrexed 13
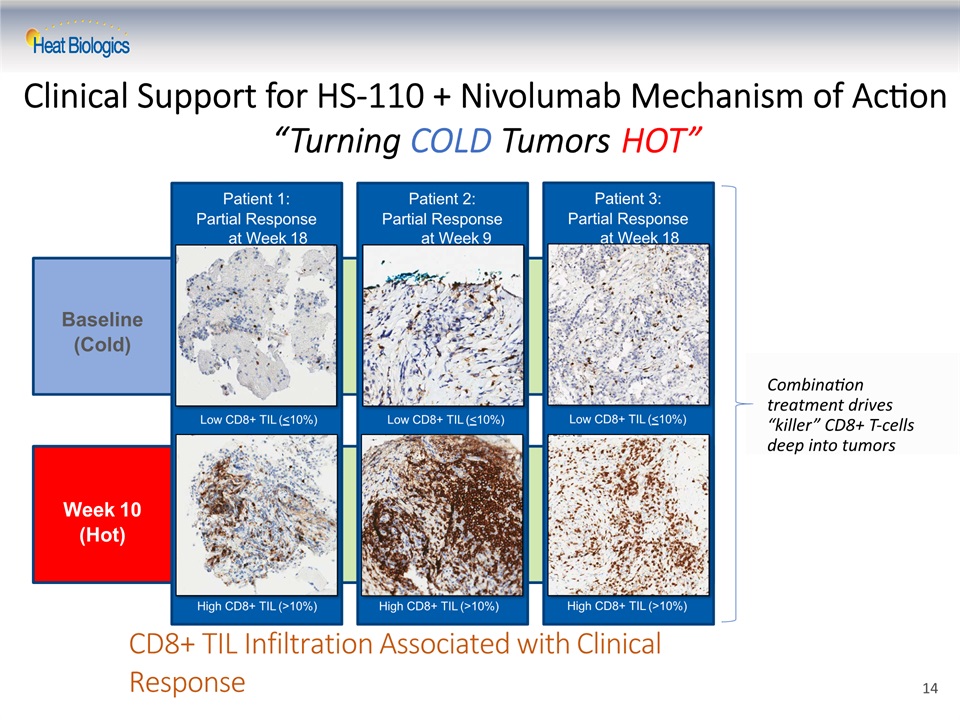
Baseline(Cold) Week 10(Hot) CD8+ TIL Infiltration Associated with Clinical Response Patient 1:Partial Response at Week 18 High CD8+ TIL (>10%) Patient 2:Partial Response at Week 9 High CD8+ TIL (>10%) Patient 3:Partial Response at Week 18 Low CD8+ TIL (<10%) High CD8+ TIL (>10%) Combination treatment drives “killer” CD8+ T-cells deep into tumors Low CD8+ TIL (<10%) Low CD8+ TIL (<10%) Clinical Support for HS-110 + Nivolumab Mechanism of Action “Turning COLD Tumors HOT” 14
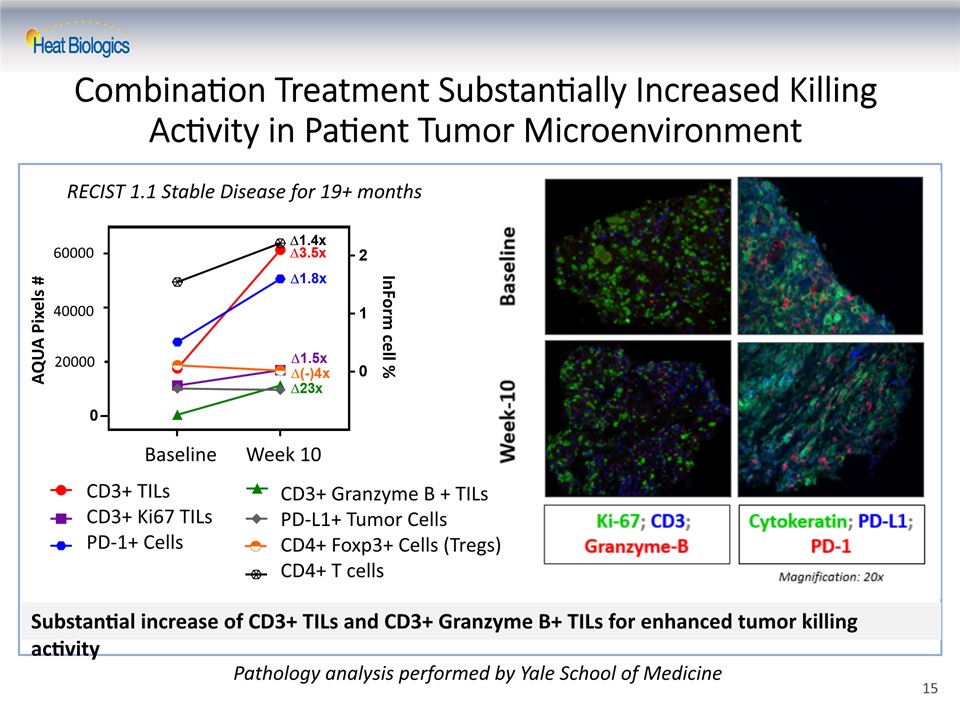
Combination Treatment Substantially Increased Killing Activity in Patient Tumor Microenvironment RECIST 1.1 Stable Disease for 19+ months Pathology analysis performed by Yale School of Medicine CD3+ TILsCD3+ Ki67 TILsPD-1+ Cells CD3+ Granzyme B + TILsPD-L1+ Tumor CellsCD4+ Foxp3+ Cells (Tregs)CD4+ T cells Baseline Week 10 60000 40000 20000 AQUA Pixels # InForm cell % Substantial increase of CD3+ TILs and CD3+ Granzyme B+ TILs for enhanced tumor killing activity 15
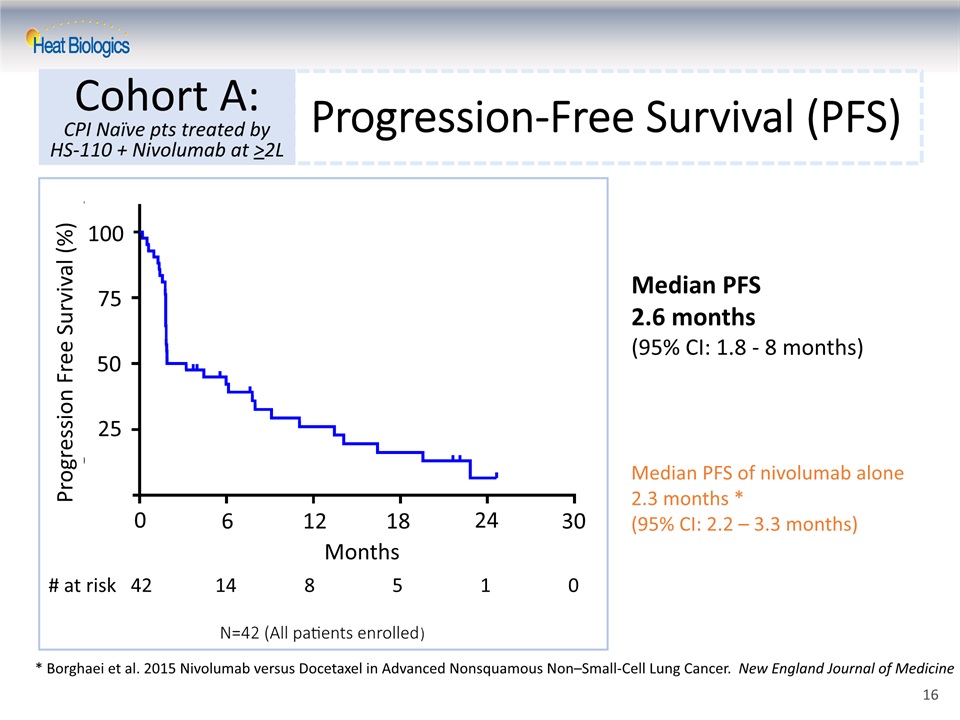
Progression-Free Survival (PFS) Cohort A:CPI Naïve pts treated by HS-110 + Nivolumab at >2L * Borghaei et al. 2015 Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. New England Journal of Medicine Median PFS2.6 months(95% CI: 1.8 - 8 months) Months 0 6 12 18 24 30 25 50 75 100 Median PFS of nivolumab alone 2.3 months *(95% CI: 2.2 – 3.3 months) Progression Free Survival (%) # at risk 42 14 8 5 1 0 N=42 (All patients enrolled) 16
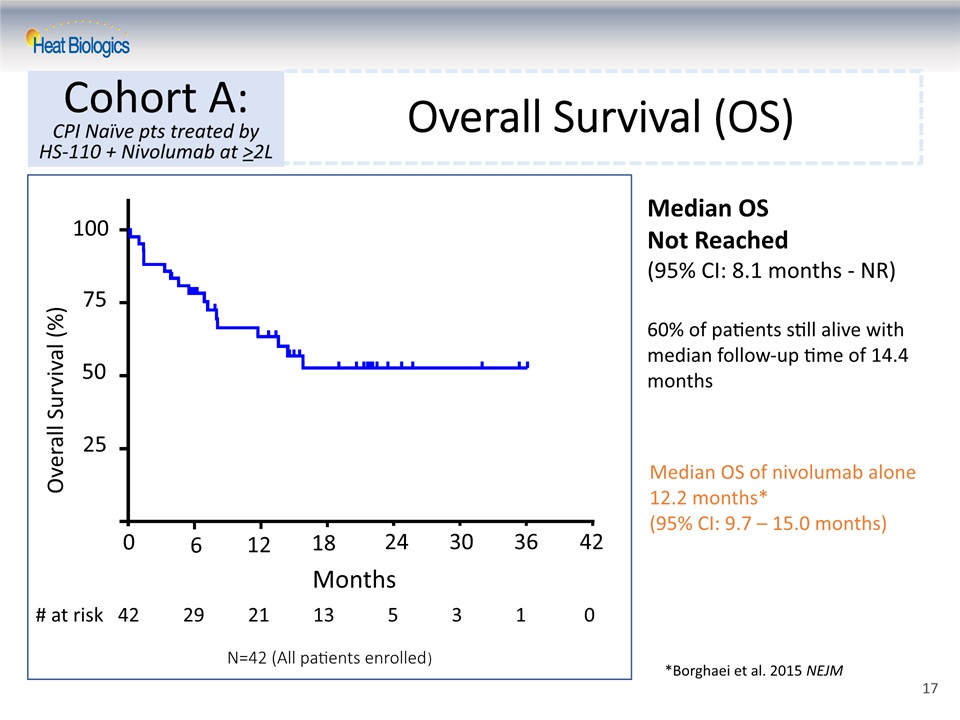
Overall Survival (%) Overall Survival (OS) Cohort A:CPI Naïve pts treated by HS-110 + Nivolumab at >2L Median OS of nivolumab alone 12.2 months*(95% CI: 9.7 – 15.0 months) *Borghaei et al. 2015 NEJM Median OS Not Reached (95% CI: 8.1 months - NR)60% of patients still alive with median follow-up time of 14.4 months Months 25 50 75 100 0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 # at risk 42 29 21 13 5 3 1 0 N=42 (All patients enrolled) 17
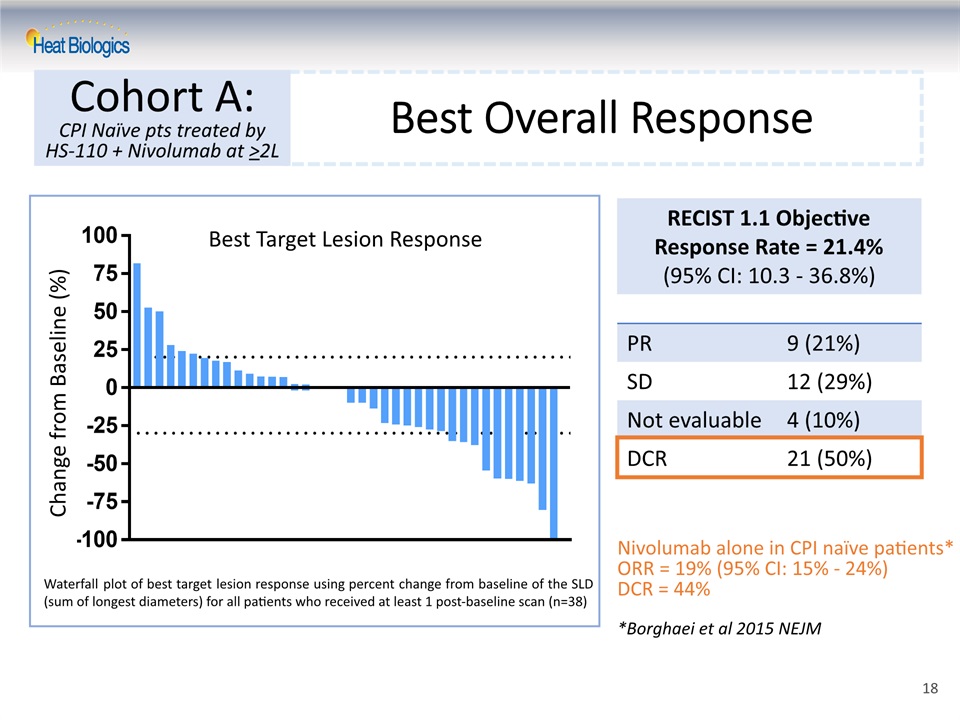
Best Target Lesion Response PR 9 (21%) SD 12 (29%) Not evaluable 4 (10%) DCR 21 (50%) RECIST 1.1 Objective Response Rate = 21.4% (95% CI: 10.3 - 36.8%) Change from Baseline (%) Best Target Lesion Response Best Overall Response Cohort A:CPI Naïve pts treated by HS-110 + Nivolumab at >2L Nivolumab alone in CPI naïve patients* ORR = 19% (95% CI: 15% - 24%)DCR = 44%*Borghaei et al 2015 NEJM Waterfall plot of best target lesion response using percent change from baseline of the SLD (sum of longest diameters) for all patients who received at least 1 post-baseline scan (n=38) 18
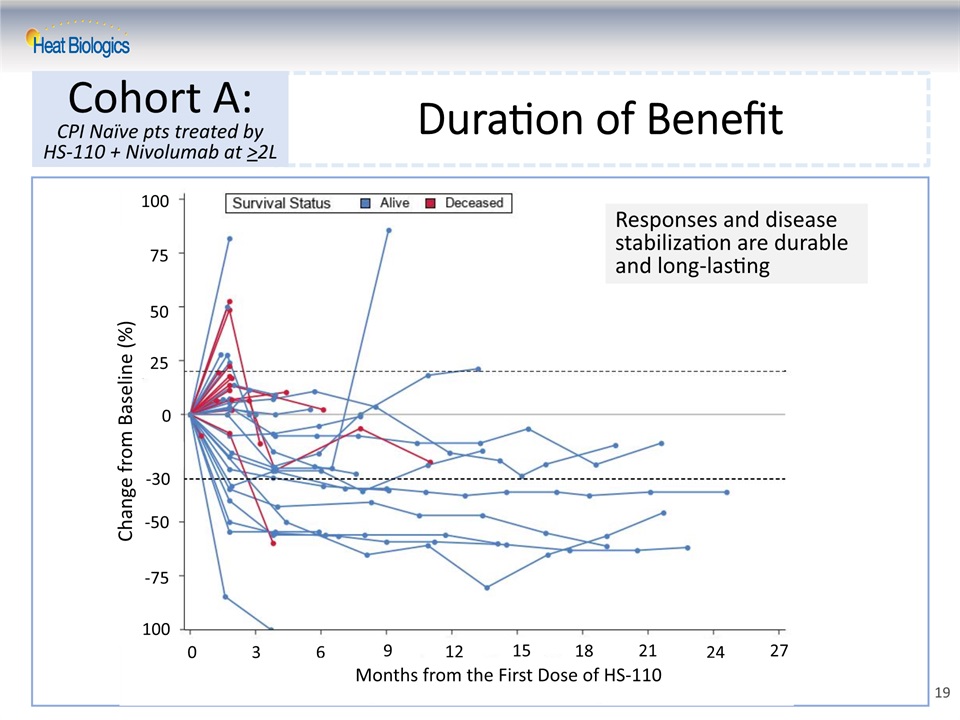
Duration of Benefit Cohort A:CPI Naïve pts treated by HS-110 + Nivolumab at >2L 19 Responses and disease stabilization are durable and long-lasting 25 50 75 100 0 -30 -50 -75 -100 Change from Baseline (%) 0 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 Months from the First Dose of HS-110
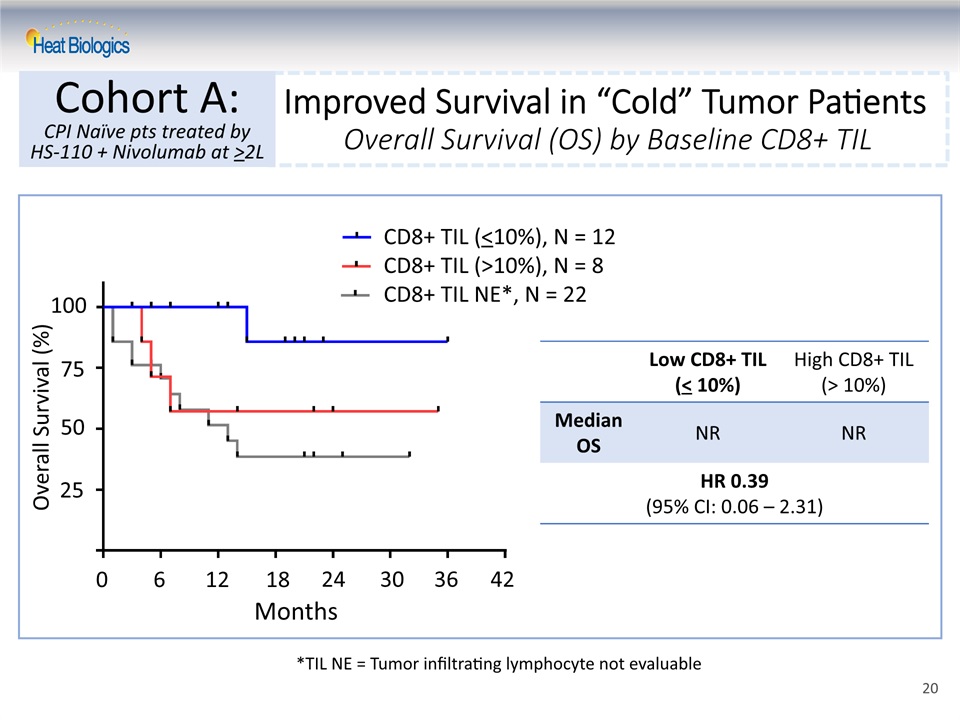
Improved Survival in “Cold” Tumor PatientsOverall Survival (OS) by Baseline CD8+ TIL Cohort A:CPI Naïve pts treated by HS-110 + Nivolumab at >2L *TIL NE = Tumor infiltrating lymphocyte not evaluable Low CD8+ TIL(< 10%) High CD8+ TIL (> 10%) Median OS NR NR HR 0.39(95% CI: 0.06 – 2.31) CD8+ TIL (<10%), N = 12CD8+ TIL (>10%), N = 8CD8+ TIL NE*, N = 22 Months 0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 25 50 75 Overall Survival (%) 100 20
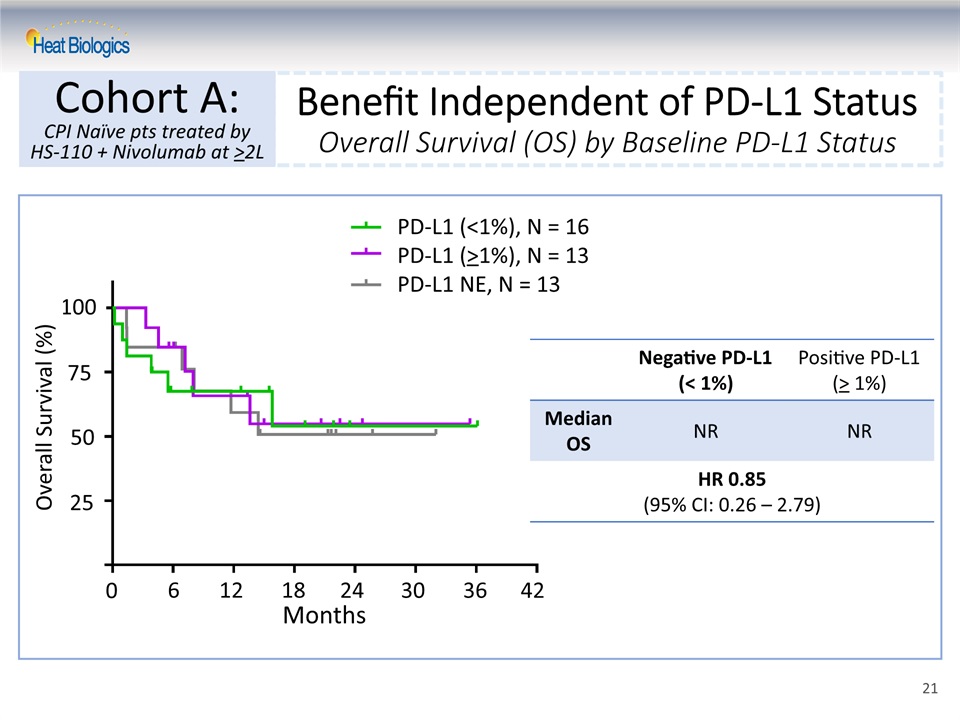
Benefit Independent of PD-L1 StatusOverall Survival (OS) by Baseline PD-L1 Status Cohort A:CPI Naïve pts treated by HS-110 + Nivolumab at >2L Negative PD-L1(< 1%) Positive PD-L1(> 1%) Median OS NR NR HR 0.85(95% CI: 0.26 – 2.79) PD-L1 (<1%), N = 16PD-L1 (>1%), N = 13PD-L1 NE, N = 13 0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 25 50 100 75 Overall Survival (%) Months 21
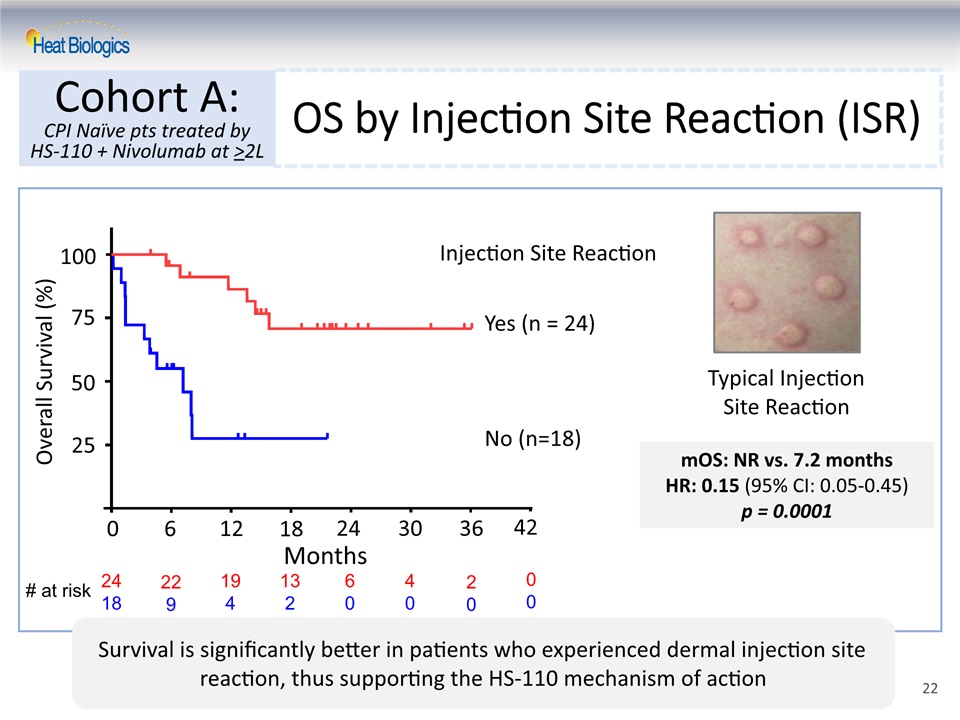
OS by Injection Site Reaction (ISR) Cohort A:CPI Naïve pts treated by HS-110 + Nivolumab at >2L Overall Survival (%) Typical Injection Site Reaction Injection Site Reaction Yes (n = 24)No (n=18) mOS: NR vs. 7.2 monthsHR: 0.15 (95% CI: 0.05-0.45)p = 0.0001 Survival is significantly better in patients who experienced dermal injection site reaction, thus supporting the HS-110 mechanism of action Months 0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 25 50 100 75 # at risk 2418 229 194 132 60 40 20 00 22
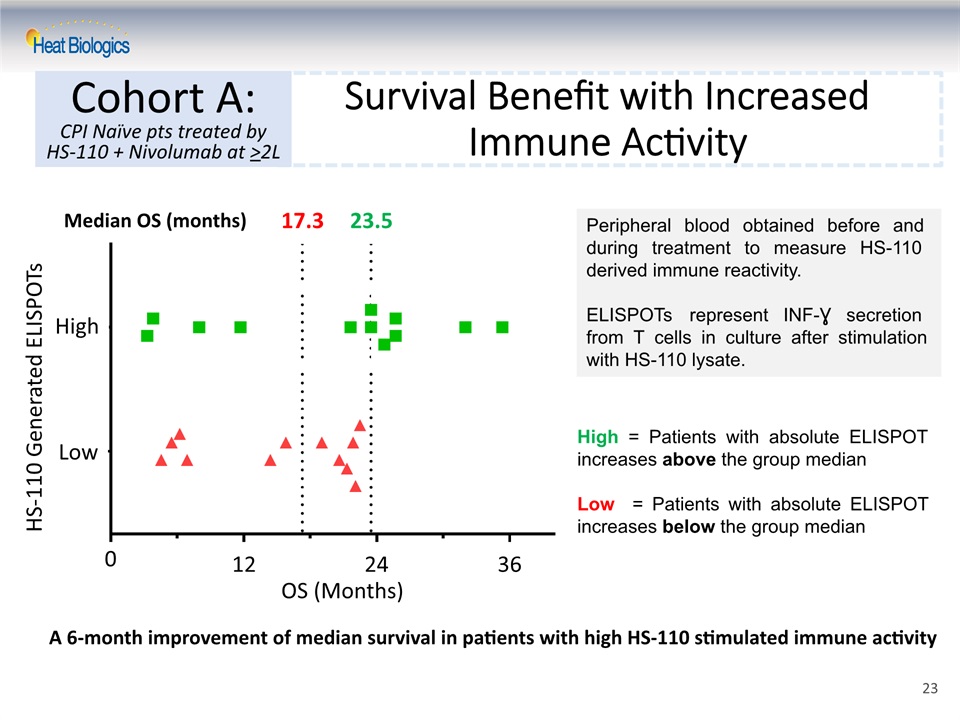
Median OS (months) 17.3 23.5 Survival Benefit with Increased Immune Activity Cohort A:CPI Naïve pts treated by HS-110 + Nivolumab at >2L OS (Months) 0 12 24 36 High Low HS-110 Generated ELISPOTs High = Patients with absolute ELISPOT increases above the group medianLow = Patients with absolute ELISPOT increases below the group median Peripheral blood obtained before and during treatment to measure HS-110 derived immune reactivity. ELISPOTs represent INF-Ɣ secretion from T cells in culture after stimulation with HS-110 lysate. A 6-month improvement of median survival in patients with high HS-110 stimulated immune activity 23
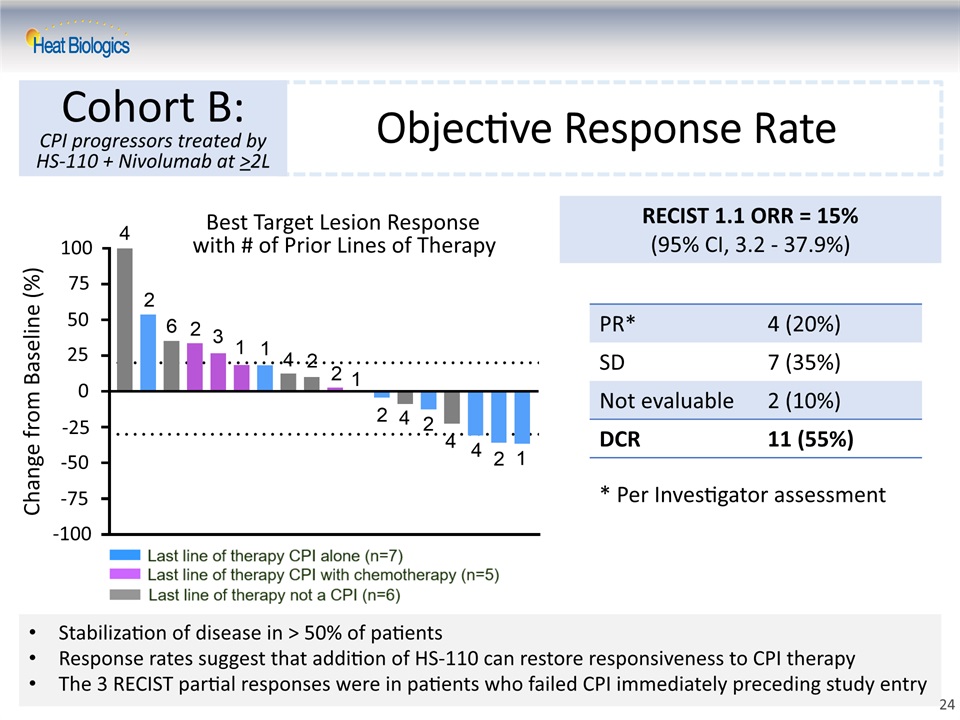
Objective Response Rate Cohort B:CPI progressors treated by HS-110 + Nivolumab at >2L RECIST 1.1 ORR = 15% (95% CI, 3.2 - 37.9%) PR* 4 (20%) SD 7 (35%) Not evaluable 2 (10%) DCR 11 (55%) Best Target Lesion Response with # of Prior Lines of Therapy 25 50 100 75 0 -25 -50 -75 Change from Baseline (%) Stabilization of disease in > 50% of patientsResponse rates suggest that addition of HS-110 can restore responsiveness to CPI therapyThe 3 RECIST partial responses were in patients who failed CPI immediately preceding study entry * Per Investigator assessment -100 24
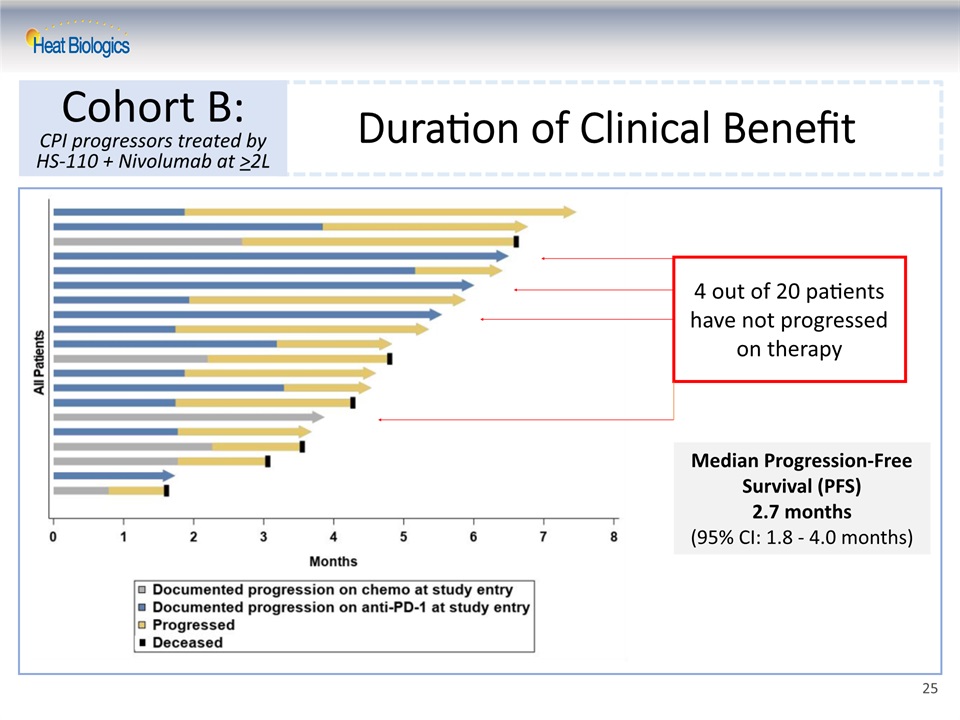
Duration of Clinical Benefit Cohort B:CPI progressors treated by HS-110 + Nivolumab at >2L Median Progression-Free Survival (PFS)2.7 months(95% CI: 1.8 - 4.0 months) 4 out of 20 patients have not progressed on therapy 25
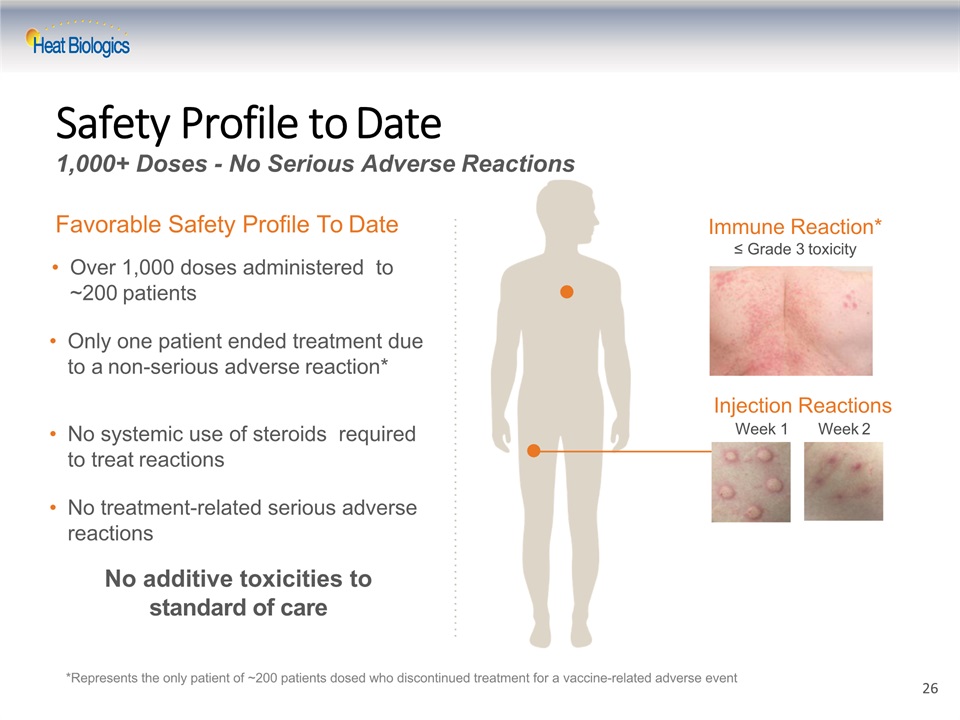
Safety Profile to Date1,000+ Doses - No Serious Adverse Reactions Over 1,000 doses administered to ~200 patients Only one patient ended treatment due to a non-serious adverse reaction* No systemic use of steroids required to treat reactionsNo treatment-related serious adverse reactions Favorable Safety Profile To Date *Represents the only patient of ~200 patients dosed who discontinued treatment for a vaccine-related adverse event Immune Reaction*≤ Grade 3 toxicity Injection ReactionsWeek 1 Week 2 No additive toxicities to standard of care 26
Summary of HS-110 Phase 2 Interim Data HS-110 in combination with nivolumab is well tolerated Preliminary results demonstrate the ability of HS-110 plus nivolumab to induce CD8+ T-cell tumor infiltration in previously “cold” tumorsIn Cohort A, the occurrence of injection site reactions and increased INF-γ ELISPOTs appears to be associated with improved overall survivalData in Cohort B suggests that the addition of HS-110 to nivolumab may restore responsiveness after tumor progression on prior checkpoint inhibitors 27

Heat acquired 80% controlling interest in Pelican in May 2017Pre-clinical synergy with Heat’s ImPACT® and checkpoint therapy$15.2M grant award from the Cancer Prevention Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT) propels PTX-35 through a 70-patient, first-in-human clinical programPTX-35 is a potential best-in-class, T-cell co-stimulator specific to “killer” CD8+ “memory” T-cells TNFRSF25 represents an emerging target in immuno-oncology Heat Biologics Acquires Pelican TherapeuticsUnlocking the Body’s Natural Defenses with a Broad Range of Combination Therapies 28
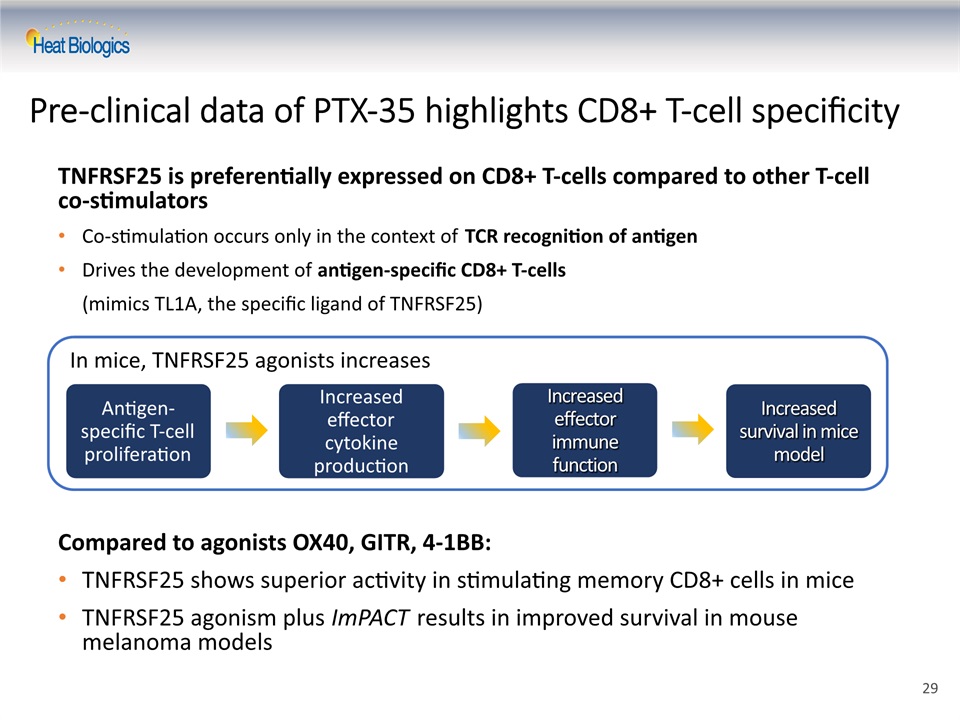
TNFRSF25 is preferentially expressed on CD8+ T-cells compared to other T-cell co-stimulatorsCo-stimulation occurs only in the context of TCR recognition of antigenDrives the development of antigen-specific CD8+ T-cells (mimics TL1A, the specific ligand of TNFRSF25)Compared to agonists OX40, GITR, 4-1BB:TNFRSF25 shows superior activity in stimulating memory CD8+ cells in miceTNFRSF25 agonism plus ImPACT results in improved survival in mouse melanoma models Pre-clinical data of PTX-35 highlights CD8+ T-cell specificity In mice, TNFRSF25 agonists increases 29
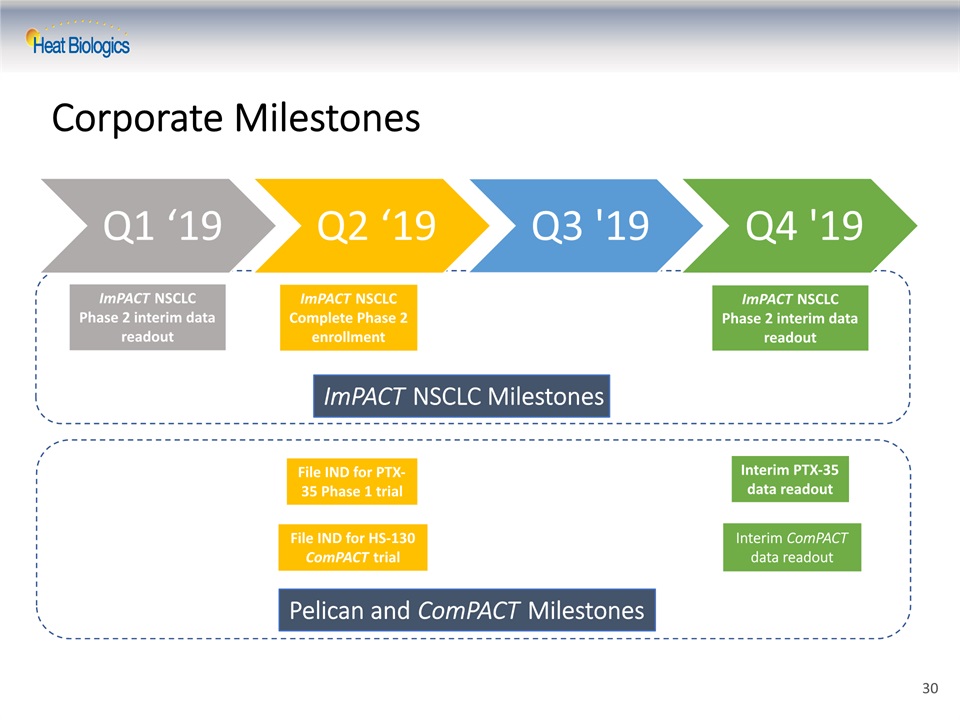
Corporate Milestones ImPACT NSCLC Phase 2 interim data readout File IND for HS-130 ComPACT trial File IND for PTX-35 Phase 1 trial ImPACT NSCLC Complete Phase 2 enrollment ImPACT NSCLC Milestones Pelican and ComPACT Milestones Interim PTX-35 data readout Interim ComPACT data readout ImPACT NSCLC Phase 2 interim data readout 30
Corporate Milestones ImPACT NSCLC Phase 2 interim data readout File IND for HS-130 ComPACT trial File IND for PTX-35 Phase 1 trial ImPACT NSCLC Complete Phase 2 enrollment ImPACT NSCLC Milestones Pelican and ComPACT Milestones Interim PTX-35 data readout Interim ComPACT data readout ImPACT NSCLC Phase 2 interim data readout 30
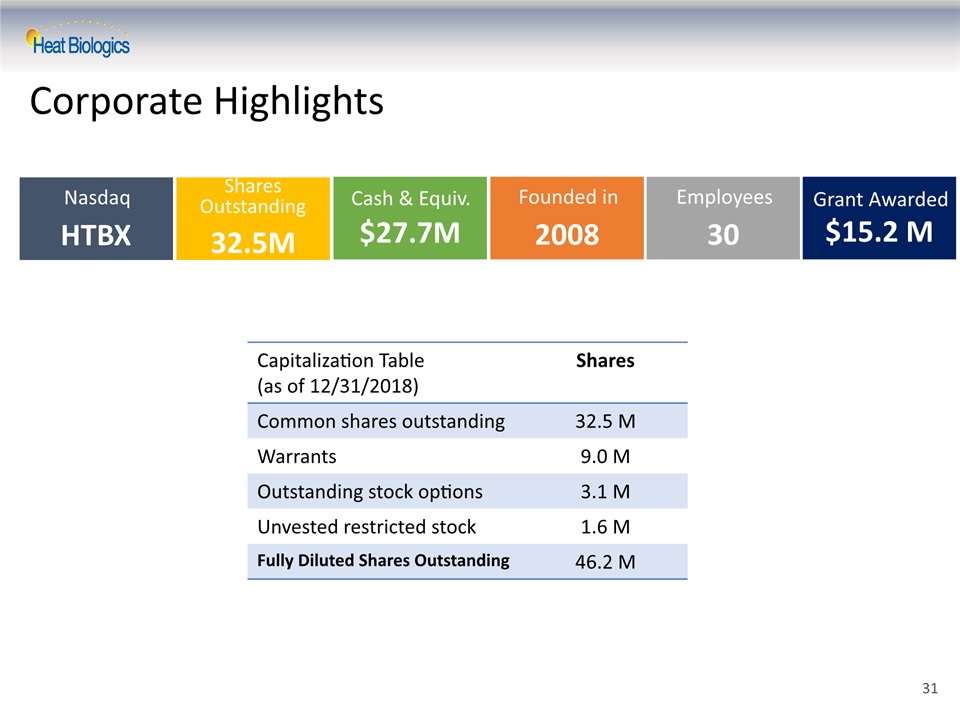
Corporate Highlights NasdaqHTBX Shares Outstanding32.5M Cash & Equiv.$27.7M Capitalization Table(as of 12/31/2018) Shares Common shares outstanding 32.5 M Warrants 9.0 M Outstanding stock options 3.1 M Unvested restricted stock 1.6 M Fully Diluted Shares Outstanding 46.2 M Founded in2008 Grant Awarded$15.2 M Employees30 31

Investment Highlights Potential Best in Class Oncology Treatment - T-cell activating platform (TCAP) produces allogeneic, off-the-shelf therapies designed to activate the immune system to turn immunologically “cold” tumors “hot”Combination Effect - Our therapies are designed to be administered with checkpoint inhibitors and other immuno-modulators to enhance immune responseOff-the-shelf Therapies - We can administer drug immediately without extracting patient material, simplifying treatment and substantially lowering cost of goodsClinical Data with Checkpoint Inhibitors (CPI) - Positive interim data from ongoing Phase 2 trial of HS-110 + CPI in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients (both CPI naïve and CPI progressors)Diverse Technology Platforms - Multiple complementary platform technologiesStrong Management Team - Senior team with broad experience in biotech, pharma, clinical development and research 32
Appendix 33
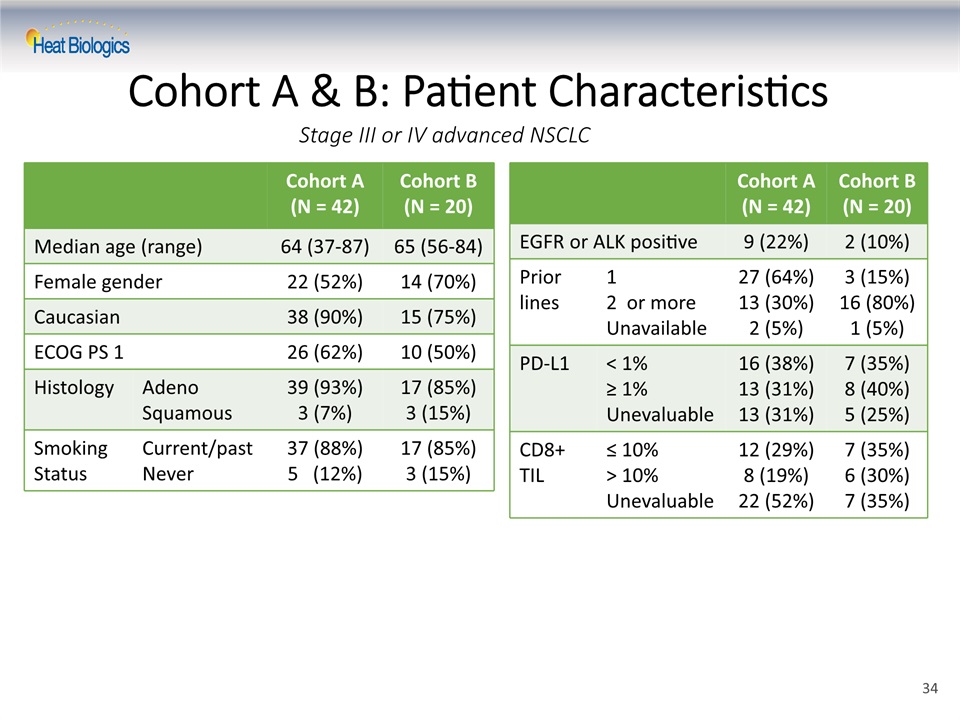
Cohort A & B: Patient Characteristics Cohort A (N = 42) Cohort B (N = 20) EGFR or ALK positive 9 (22%) 2 (10%) Prior lines 12 or more Unavailable 27 (64%)13 (30%)2 (5%) 3 (15%)16 (80%)1 (5%) PD-L1 < 1%≥ 1%Unevaluable 16 (38%)13 (31%)13 (31%) 7 (35%)8 (40%)5 (25%) CD8+ TIL ≤ 10%> 10%Unevaluable 12 (29%)8 (19%)22 (52%) 7 (35%)6 (30%)7 (35%) Cohort A (N = 42) Cohort B (N = 20) Median age (range) 64 (37-87) 65 (56-84) Female gender 22 (52%) 14 (70%) Caucasian 38 (90%) 15 (75%) ECOG PS 1 26 (62%) 10 (50%) Histology AdenoSquamous 39 (93%)3 (7%) 17 (85%)3 (15%) Smoking Status Current/pastNever 37 (88%)5 (12%) 17 (85%)3 (15%) Stage III or IV advanced NSCLC 34
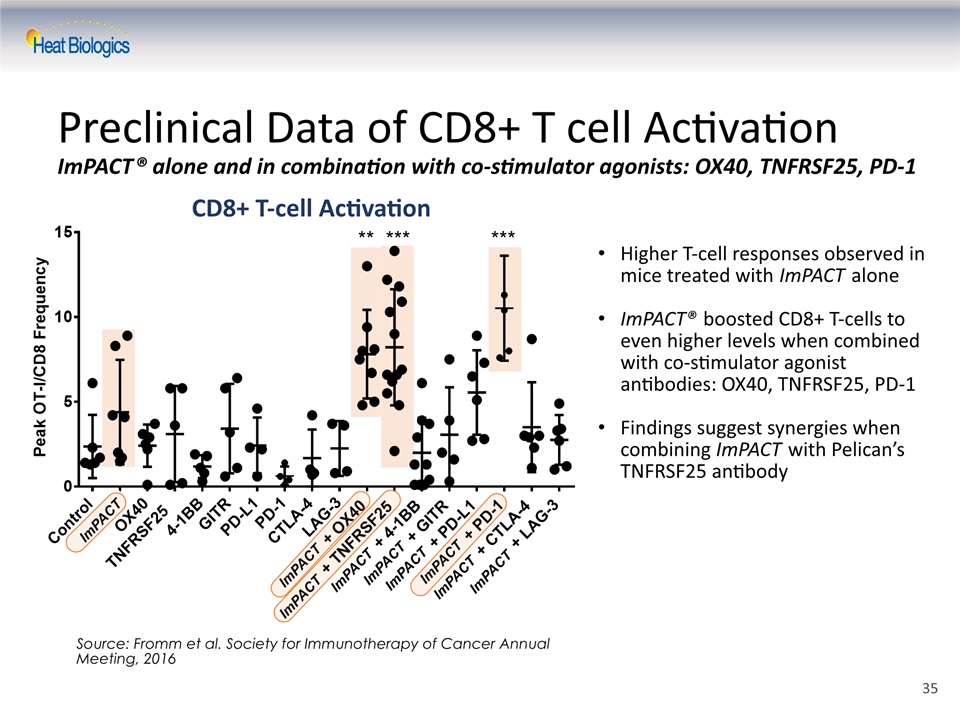
Preclinical Data of CD8+ T cell ActivationImPACT® alone and in combination with co-stimulator agonists: OX40, TNFRSF25, PD-1 Source: Fromm et al. Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer Annual Meeting, 2016 Higher T-cell responses observed in mice treated with ImPACT aloneImPACT® boosted CD8+ T-cells to even higher levels when combined with co-stimulator agonist antibodies: OX40, TNFRSF25, PD-1Findings suggest synergies when combining ImPACT with Pelican’s TNFRSF25 antibody ImPACT ImPACT CD8+ T-cell Activation ImPACT ImPACT ImPACT ImPACT ImPACT ImPACT ImPACT 35

ComPACT™ Platform Technology gp96-Ig OX40L-Fc The first potential dual-acting immunotherapy designed to deliver T-cell activation andco-stimulation in a single product – combination therapy without additive costs 36
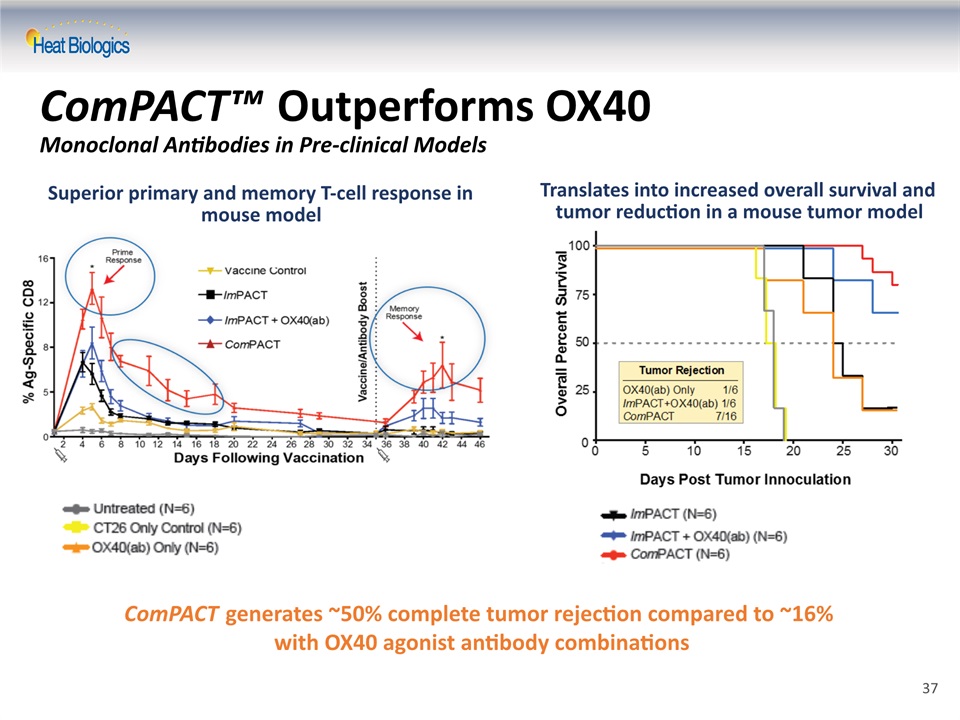
ComPACT™ Outperforms OX40 Monoclonal Antibodies in Pre-clinical Models ComPACT generates ~50% complete tumor rejection compared to ~16% with OX40 agonist antibody combinations Superior primary and memory T-cell response in mouse model Translates into increased overall survival and tumor reduction in a mouse tumor model 37

TNFRSF25 - An Emerging Target for T-cell Co-stimulation 38 Target Companies Co-stimulator Combinations 4-1BB Pfizer, ISA Pharma, Gilead, Bristol Myers, Inhibrx, Immatics, Pieris, NCI Phase 1/2Combinations: Chemotherapy, epigenetic modulator, CD20 mAb, HPV vaccine, CART, PD-L1, BTK, Herceptin, modified CD8+ T cells, IL-2, CSF1R, LAG-3, bispecific w/ HER-2, two co-stimulators (w/ OX40) OX40 MedImmune, GSK, Incyte, Genentech, Pfizer, AbbVie, Bristol Myers, Alligator Bio Phase 1/2OX-40 prior to surgery. Other combinations: PD-1, PD-L1, CTLA4, axitinib, 41BB, smoothened inhibitor Anti-CD33, azacitidine, TLRs, bi-specifics of OX40 and CTLA-4 GITR Novartis, Incyte-Agenus, MedImmune, Leap Therapeutics, BMS, OncoMed Phase 1Combinations: PD-1, Fc disabled co-stimulation, hexameric GITR ligand, IDO inhibitor, CTLA-4, GITR ligand-fusion CD27 Celldex-BMS, Merck-Aduro Phase 1/2Combinations: PD-1/L-1, sunitinib, CD20, melanoma vaccine, TL3 agonist ICOS Celgene-Jounce, GSK Phase 1/2Combinations: PD-1, CTLA4, docetaxel TNFRSF25 Heat (under Pelican) Filing IND in Q2 2019 in advanced solid tumors. Combination studies being planned TNFRSF25 is a potential best-in-class T cell co-stimulator due to its preferential specificity to ‘memory’ CD8+ T cells Pelican is the only company with a disclosed program targeting TNFRSF25
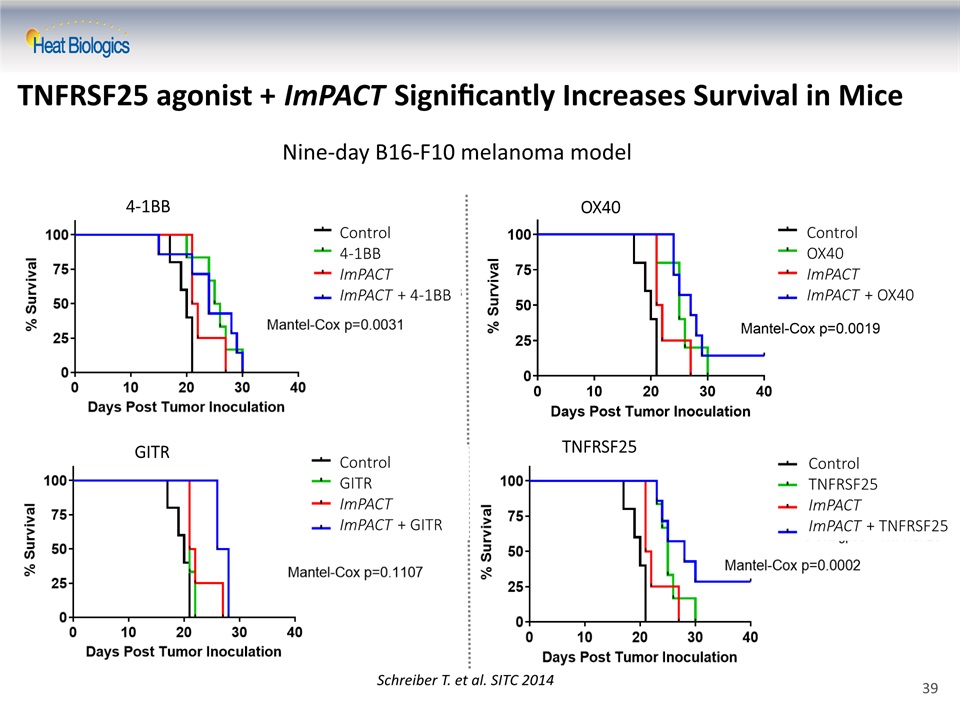
TNFRSF25 agonist + ImPACT Significantly Increases Survival in Mice OX40 GITR 4-1BB TNFRSF25 Schreiber T. et al. SITC 2014 Control4-1BBImPACTImPACT + 4-1BB ControlOX40ImPACTImPACT + OX40 ControlGITRImPACTImPACT + GITR ControlTNFRSF25ImPACTImPACT + TNFRSF25 39 Nine-day B16-F10 melanoma model
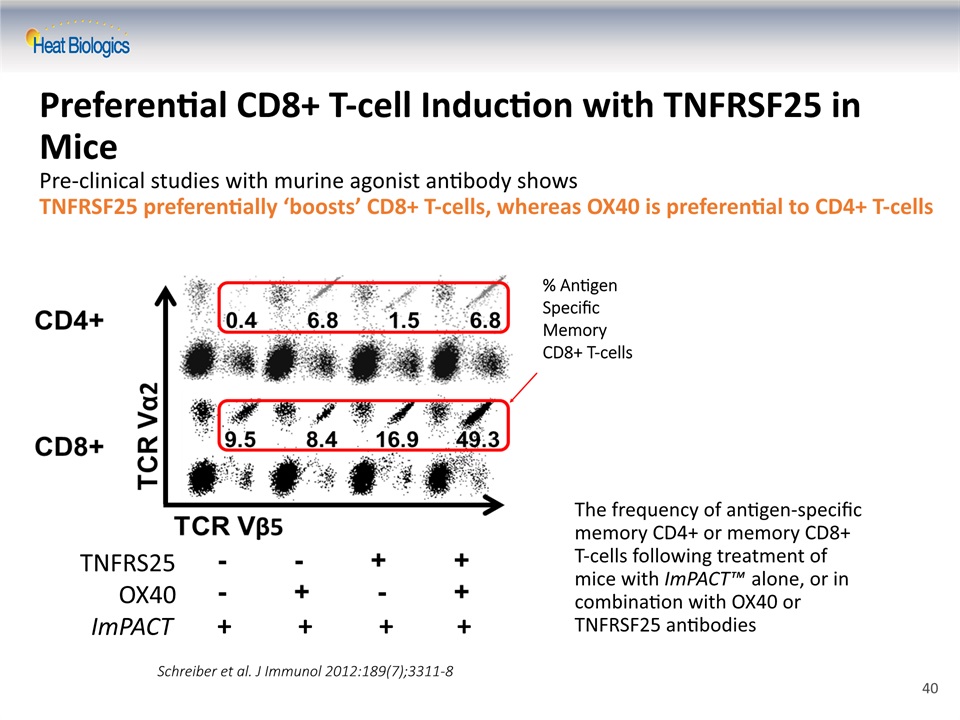
Preferential CD8+ T-cell Induction with TNFRSF25 in MicePre-clinical studies with murine agonist antibody shows TNFRSF25 preferentially ‘boosts’ CD8+ T-cells, whereas OX40 is preferential to CD4+ T-cells The frequency of antigen-specific memory CD4+ or memory CD8+ T-cells following treatment of mice with ImPACT™ alone, or in combination with OX40 or TNFRSF25 antibodies Schreiber et al. J Immunol 2012:189(7);3311-8 % AntigenSpecific Memory CD8+ T-cells TNFRS25 OX40 ImPACT + + + + 40
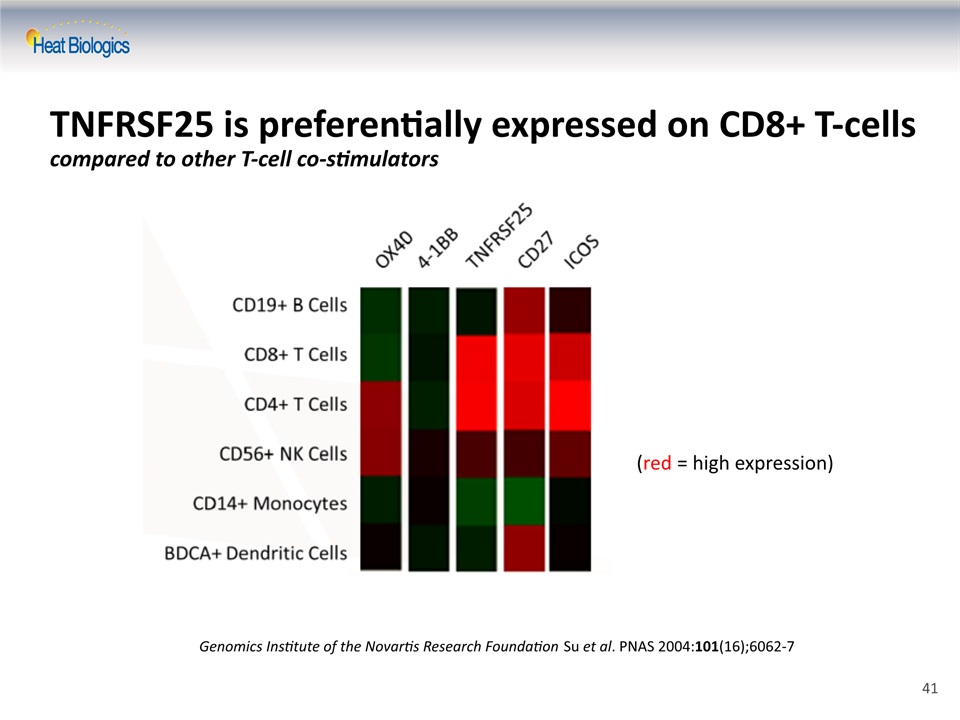
TNFRSF25 is preferentially expressed on CD8+ T-cellscompared to other T-cell co-stimulators Genomics Institute of the Novartis Research Foundation Su et al. PNAS 2004:101(16);6062-7 (red = high expression) 41
Management and Advisors Jeff WolfFounder & CEO Ann RosarVP of Finance Janice McCourtVP of Business Devt. Lori McDermottVP of Clinical Dev. Gary VinsonVP of Manufacturing Jeff Hutchins, Ph.D.CSO/COO George Peoples, MDChief Medical Advisor Management Scientific Advisors Robert Levy, Ph.D.University of Miami Roger Cohen, MDUniversity of Pennsylvania Robert Negrin, MDStanford University Llew Keltner, MD, Ph.D.Epistat Anthony Tolcher, MDNext Oncology Gary Acton, MDAdvisor Board of Directors Jeff WolfFounder, Chairman and CEO John Prendergast, Ph.D.Lead Independent Director John Monahan, Ph.D.Director Edward SmithDirector 42